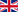
Figure 2. Different types of intellectual properties
These intellectual properties are often called industrial properties, but these are not hard-and-fast boundaries of what is included, therefore it is easier to say other intellectual properties. Also, there are a few intellectual assets which cannot be protected.
Intellectual properties: Watch the video 'Crash course in IP'
Usually IP experts distinguish between copyright and the other intellectual properties, because copyright is used to protect any original – mostly – artwork and you do not have to apply for it, while industrial properties intangible property right in the field of agriculture, commerce and industry and also they have to applied for. A small addition is that you can’t copyright a brand name consisting of only one word, but you can apply for a trademark.
There are several forms of intellectual properties all of which share the same goal: to promote creativity and innovation by expressing the right of the creators and innovators in their creations and innovations by claiming monopoly to utilization.
Here are a few examples of intellectual properties in your daily work:
Patent
A patent – the most well-known of all intellectual property types - contains a new technical solution for a product or process; you cannot patent however the idea behind it: a new rocket fuel can be patented but the notion of the rocket cannot. Therefore a patent cannot be something obvious, it has to be novel and it should be useful to the industry.
A patent not only describes the invention but what it does and how. These parts of the patents are called patent claims, and they are there to outline the activities and processes included in the patent. If there is something included in a valid patent, then another invention doing the same thing would be an infringement of said patent. The exclusive rights prevent third parties from manufacturing, using and offering the product, or in case of a process patent the use of the process is prohibited.
Patents last for a certain period of time – usually 20 years - after which the patent becomes public domain. (NTP vs Blackberry case study for example http://www.infotoday.com/IT/may06/Pike.shtml)
Trademark
The trademark is a graphically depicted, registered sign that serves to distinguish between the goods and services, to differentiate between companies, to display a certain quality or to stimulate sales. There is 3 main branch of trademark: collective marks for members of an association, certification marks for complying with a certain defined standard and service marks used by for example hotels, car-rental agencies.
Trade name
Trade name ( business name ) is usually strongly tied to the trademark, it does not need however specific protection whether it is a part of a specific trademark. The trade name identifies the company and it should not be used by another company.
Industrial design
The primarily aesthetic appearance of the whole or part of a product is protectable via industrial design, if the design is original or new. Another key criterion is that it should be able to be reproduced by industrial means. The maximum term is usually somewhere between 10 and 25 years.
Layout design of integrated circuits
The protection of the topography of integrated circuits, i.e. the arrangement of chip of semiconductor devices. These designs need protection because they are easy to copy but very costly to develop.
Geographical indications
The GI is used to indicate the origin of a certain product or to certify that a product originates from a particular area to meet certain standards. It is very like a trademark.
Database rights
It is very like copyright, but it exists to recognize the effort put into compiling a database.
Trade dresses
It generally means the aesthetic appearance of a product or its packaging that distinguishes a product from others and tells the customers its origins.
Plant varieties
It grants the commercial right to sell a new breed of a plant. It gives the breeder exclusive rights over the new plant (over the propagating and the harvested material as well).
Important :
To obtain a patent or a registered trademark does not mean the protection itself. Patenting means disclosure of the invention and claiming exclusive use for a certain period of time (a maximum of 25 years). The protection is provided by IPR law, therefore it does not make sense to apply for a patent in those countries where the law cannot guaranty the claimed rights.
Other intellectual assets that could not be protected by law (non-IP) are the following:
Know-how
Know-how is a practical knowledge which is very difficult to transfer. It is always a part of technology transfer activities but it is not protected in any country apart from the U.S. Know-how can be protected however in contracts and license agreements by defining the scope of confidential information and non-disclosure.
Trade secrets
Trade secrets are generally not known to the public and represent significant economic advantage. The contribution to a company’s value is very hard to estimate due to their secrecy. They are not protected by disclosing them to the public but keeping their confidentiality: there are special procedure for handling them, non-disclosure agreements and there may be physical barriers protecting them.